What is the digestive tract? A long continuous tube with food first entering it at the mouth.
What happens to undigested materials in the digestive tract?
Sketch the path that food takes through the digestive tract. Be sure to include the mouth, esophagus, stomach, duodenum, small intestine, appendix, large intestine rectum, and all 4 sphincters.
What is the function of the mouth in the digestion process? The teeth and tongue begin the mechanical breakup of food and mix it with saliva.
What is the term for the small mass of food that enters into the esophagus? bolus
What triggers peristalsis? presence of the bolus in the esophagus triggers peristalsis.
What is the function of the cardiac sphincter? Closes the entrance to the stomach and prevents its contents from re-entering the esophagus
What is the mucous membrane? protective mucous coating which prevents digestion
How long is the small intestine? 20 feet long
Where does most digestion and absorption of nutrients take place? small intestine
What increase the surface area of the small intestine? villi
What is the first section of the small intestine? What is its function?
Where is bile stored? gallbladder
What is segmentation? grabbing of a tube tightly at various places around the middle and squeezing so its contents are broken into smaller pieces.
When does the ileocecal sphincter open? when the food builds up in the small intestin
What is the function of the anal sphincter? Stops waste from leaving body until you make it
What is the function of the appendix in humans?
Where does digestion begin? mouth
What is gastric juice made of? Hydrochloric acid and enzymes
Where are enzymes released in the small intestine produced? the pancreas
What is the function of the following enzymes: amylase, lactase, maltase, sucrase, and lipase? enzymes
There are two ways that nutrients get into the blood stream. Describe each method.
Wednesday, April 16, 2008
Wednesday, April 9, 2008
Hormonal Control of the Menstrual Cycle worksheet
1.What is a hormone? Any of various internally secreted compounds, as insulin or thyroxine, formed in endocrine glands, that affect the functions of specifically receptive organs or tissues when transported to them by the body fluids.
2.What system is responsible for the production of hormones? The reproductive system.
3.Sketch a picture of the female reproductive system. Include the oviduct, ovaries, uterus, cervix and vagina.
4.Where does the embryo undergo most of its development? The uterus
5.What is another name for the fallopian tube? The cervix
6.Where does fertilization take place? The ovaries
7.What is ovulation? To produce and discharge eggs from an ovary or ovarian follicle.
8.What is the follicle converted to? The corpus luteum.
9.What happens during the flow phase? The uterine lining sloughs off.
2.What system is responsible for the production of hormones? The reproductive system.
3.Sketch a picture of the female reproductive system. Include the oviduct, ovaries, uterus, cervix and vagina.
4.Where does the embryo undergo most of its development? The uterus
5.What is another name for the fallopian tube? The cervix
6.Where does fertilization take place? The ovaries
7.What is ovulation? To produce and discharge eggs from an ovary or ovarian follicle.
8.What is the follicle converted to? The corpus luteum.
9.What happens during the flow phase? The uterine lining sloughs off.
The Urinary Worksheet
What are three functions of the kidneys? Filters all matter not just waste products. Selectively reabsorbs all the substances that the body can make of use. Eliminates waste products from the blood in the form of urine.
What is the protective layer around the kidney? The peri-renal capsule.
What is the outer layer of the kidney? The cortex.
What is the urine collection system of the kidney? The medulla.
What is the dilated end of the ureters called? The pelvis.
What is the protective layer around the kidney? The peri-renal capsule.
What is the outer layer of the kidney? The cortex.
What is the urine collection system of the kidney? The medulla.
What is the dilated end of the ureters called? The pelvis.
What is the function of the bladder? To store urine.
What transports urine in males? Females? Male/Urethra- transports urine to the outside of the body. It also carries semen. Female/Urethra- Only transports urine to the outside of the body.
Monday, April 7, 2008
Basic Resperatory Worksheet

What are the two entrances for oxygen to enter the respiratory system? Nose and mouth.
Where does the air go to from the nose and mouth? Pharynx.
In between the pharynx and the trachea what structure does this lesson leave out? The larynx.
Where is the trachea located in reference to the esophagus? Anterior.
What structures moisten the air in the Respiratory System? Nose and mouth.
What is the name for the small air sacs at the end of the bronchioles? The alveoli.
Where does gas exchange take place in the lungs? In the alveoli.
What is the main muscle of respiration? Diaphragm.
What happens when we inhale? The diaphragm contracts, lowering the air pressure in the lungs, allowing them to take in air. Exhale? The diaphragm relaxes, increasing the air pressure so the lungs release air.
Where does the air go to from the nose and mouth? Pharynx.
In between the pharynx and the trachea what structure does this lesson leave out? The larynx.
Where is the trachea located in reference to the esophagus? Anterior.
What structures moisten the air in the Respiratory System? Nose and mouth.
What is the name for the small air sacs at the end of the bronchioles? The alveoli.
Where does gas exchange take place in the lungs? In the alveoli.
What is the main muscle of respiration? Diaphragm.
What happens when we inhale? The diaphragm contracts, lowering the air pressure in the lungs, allowing them to take in air. Exhale? The diaphragm relaxes, increasing the air pressure so the lungs release air.
Thursday, April 3, 2008
Basic Nervous System Anatomy Worksheet
What does CNS and PNS stand for? Central Nervous System and Peripheral Nervous System.
What are the parts of the CNS? The brain and spinal chord.
Describe something that you do on a regular basis that your PNS controls. Digest food.
What are the two divisions of the autonomic nervous system and what does each control?Sympathetic Nervous System - controls the body in times of stress, worry, fear, and emergency.Parasympathetic Nervous System - brings the body to a normal state and allows for rest and relaxation.
What are the three main types of neurons? What is the function of each?Sensory Neuron - conducts impulses from the body to the CNS.Motor Neuron - conducts impulses from CNS to effector organ.Interneuron - conducts impulses within the CNS.
What is the function of the axon of a nerve cell? Sends out the impulses. The dendrite? Recieves the impulses.
What is a synapse? The transfer of impulses from the dendrite of one neuron to the axon of another neuron over the synaptic gap.
What are the parts of the CNS? The brain and spinal chord.
Describe something that you do on a regular basis that your PNS controls. Digest food.
What are the two divisions of the autonomic nervous system and what does each control?Sympathetic Nervous System - controls the body in times of stress, worry, fear, and emergency.Parasympathetic Nervous System - brings the body to a normal state and allows for rest and relaxation.
What are the three main types of neurons? What is the function of each?Sensory Neuron - conducts impulses from the body to the CNS.Motor Neuron - conducts impulses from CNS to effector organ.Interneuron - conducts impulses within the CNS.
What is the function of the axon of a nerve cell? Sends out the impulses. The dendrite? Recieves the impulses.
What is a synapse? The transfer of impulses from the dendrite of one neuron to the axon of another neuron over the synaptic gap.
The Heart Worksheet
All vertebrates have what type of circulatory system? Closed circulatory system.
How does the circulatory system maintain homeostasis? Through water and electrolyte transport, fluid volume control, and regulation of pH and of body temperature.
Name 4 functions of the circulatory system. Transports nutrients to cells, maintains homeostasis, carries hormones to regulate certain body functions, transports gases, and transports antibodies to fight infection.
What are blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart called? Arteries.
What are blood vessels that carry blood to the heart called? Veins.
What is the sac that surrounds the heart called? The pericardium.
What is the muscular portion of the heart called? Myocardium.
What is the lining of the myocardium called? Endocardium
What is the name of the upper cavities of the heart? Atria. The lower cavities? Ventricles.
What veins carry blood to the left atrium? The Pulmonary Vein. The right atrium? Superior and Inferior Vena Cava.
What arteries carry blood away from the left ventricle? Aorta. The right ventricle? Pulmonary Artery.
How does the circulatory system maintain homeostasis? Through water and electrolyte transport, fluid volume control, and regulation of pH and of body temperature.
Name 4 functions of the circulatory system. Transports nutrients to cells, maintains homeostasis, carries hormones to regulate certain body functions, transports gases, and transports antibodies to fight infection.
What are blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart called? Arteries.
What are blood vessels that carry blood to the heart called? Veins.
What is the sac that surrounds the heart called? The pericardium.
What is the muscular portion of the heart called? Myocardium.
What is the lining of the myocardium called? Endocardium
What is the name of the upper cavities of the heart? Atria. The lower cavities? Ventricles.
What veins carry blood to the left atrium? The Pulmonary Vein. The right atrium? Superior and Inferior Vena Cava.
What arteries carry blood away from the left ventricle? Aorta. The right ventricle? Pulmonary Artery.
Tuesday, April 1, 2008
Basic Eye Anatomy Worksheet

The eye is part of which nervous system? Central.
What types of tissues give the eye protection? Fatty and connective.
What structure in the eye produces tears? Lacrimal glands.
What acts as an antibacterial layer in the eye? The conjunctiva
What is the cornea? The anterior portion of the sclera
What layer of the eye contains the rods and cones? The retina
What is the function of the rods? The cones? Rods-for night vision; Cones-for daylight vision and color vision
What is the colored part of the eye? The iris
What structure allows light to enter the eye? The pupil
Sketch picture of eye with following labeled: lacrimal glands, eyelashes, iris, pupil, cornea, lens, eyelid, sclera, choroids, optic nerve, and retina
Sunday, March 30, 2008
Basic Nervous SYstem Anatomy
 What does CNS and PNS stand for? Central Nervous System and Peripheral Nervous System!
What does CNS and PNS stand for? Central Nervous System and Peripheral Nervous System!What are the parts of the CNS? brain and spiral cord and it controls thinking, memory and behavior.
Describe something that you do on a regular basis that your PNS controls. carry messages through out the body.
What are the two divisions of the autonomic nervous system and what does each control? Sympathetic branch controls the body in times of stress, worry, fear,and emergency. Parasympatic branch brings the body back to a normal state and allows for rest and relaxation to occur.
What are the three main types of neurons? sensory neuron, motor neuron, and interneuron!
What is the function of each? interneuron only conducts within the CNS. motor neurons takes the impulse from the CNS to the foot for actions. sensory neuron conduct the impulse from the foot to the CNS.
What is the function of the axon of a nerve cell? The dendrite?
What is a synapse? simply the conduction of an impulse from one neuron to another.-Sketch a neuron and label the axon and the dendrite. (above)
Baisc Ear Anatomy Worksheet
 1. Sketch a picture of an ear and label the following: (above)
1. Sketch a picture of an ear and label the following: (above)Inner ear
middle ear
outer ear
pinna
tympanic membrane
cochlea
stapes
malleusincus
2. What is the function of the following:Pinna- cartilage flap that conveys sounds waves into the ear.
tympanic membrane - converts sounds waves into sound vibrations.
ossicles - three small bones which magnify sound vibrations
cochlea - contains fluid and changes sound vibrations into nerve impules.
semicircular canals - sends impulses to the brain to let it know your body is off balance.
3. What three bones make up the ossicles? - incus -stapes - malleus
4. What is the function of hairs in the ear? stimulate nerve impulses to be sent to the brain by way of the auditory nerve.
Monday, March 3, 2008
Basic Skeletal Anatomy Worksheet

1.Describe the 4 functions of bones. supporting the body, protecting internal organs, produce blood cells, and provide muscle attachment .
2.How many bones are there in the human body? 206
3.What are the two divisions of the skeletal system? Name 5 specific bones in each division.
4.What bone makes up the upper arm? humerus
5.What bone makes up the face? facial bone
6.Name two bones that protect vital internal organs. ribs, and vertebral column
7.What bone in the forearm is always on thumb side? radius
8. What bone is movable for back muscles to attach to?vertebral column
9. What bone is also known as the shin bone? tibia
10. Sketch a human skeleton and label the following bones: skull, clavicle, sternum, humerus, radius, ulna, patella, femur, tibia, fibula, pelvis, vertebral column, scapula and rib cage.
Basic Joint Anatomy Worksheet
1.Why is there little to no movement in a fibrous joint?Because the bones making up the joint are united with strong fibrous tissue.
2.What is an example of a fibrous joint? sutures which hold the bones in the skull
3.Describe a cartilaginous joint and give an example. where bones are united by intervening fibrocartilage- vertebrae of the spinal column are joined by intervertebral discs
4.What type of joint essentially allows free movement? synovial joints
5. What lubricates a joint cavity? Synovial fluid.
6.For the following joint types please list the name of the joint type, the type of movement of the joint, the shape of the joint and an example.
7.Plane joint- synovial, gliding or slipping, slighlty curved articular surfaces, carpal bones in the hand
8.Hinge joint- synovial, movement is limited to rotate around a single axis, irregular cylinder and a concave groove, elbow joint
9.Condylar joint-synovial, similar to hinge but also as other movements, has 2 aticular surfaces, the knee joint
10.Ball and Socket joint- synovial, spherical articulation, movement in variety of directions, the shoulder joint
11.Ellipsoidal joint- synovial, oval ball and socket, variety of direct, wrist jointPivot joint- synovial, bony peg, rotate with respect to the other, joints between the radius and ulna
Saddle joint- synovial, 2 western saddles, articulating surfaces concave in one direction and convex in the other, movement in variety of directions, joint at base of the thumb.
2.What is an example of a fibrous joint? sutures which hold the bones in the skull
3.Describe a cartilaginous joint and give an example. where bones are united by intervening fibrocartilage- vertebrae of the spinal column are joined by intervertebral discs
4.What type of joint essentially allows free movement? synovial joints
5. What lubricates a joint cavity? Synovial fluid.
6.For the following joint types please list the name of the joint type, the type of movement of the joint, the shape of the joint and an example.
7.Plane joint- synovial, gliding or slipping, slighlty curved articular surfaces, carpal bones in the hand
8.Hinge joint- synovial, movement is limited to rotate around a single axis, irregular cylinder and a concave groove, elbow joint
9.Condylar joint-synovial, similar to hinge but also as other movements, has 2 aticular surfaces, the knee joint
10.Ball and Socket joint- synovial, spherical articulation, movement in variety of directions, the shoulder joint
11.Ellipsoidal joint- synovial, oval ball and socket, variety of direct, wrist jointPivot joint- synovial, bony peg, rotate with respect to the other, joints between the radius and ulna
Saddle joint- synovial, 2 western saddles, articulating surfaces concave in one direction and convex in the other, movement in variety of directions, joint at base of the thumb.
Thursday, February 28, 2008
Tuesday, February 5, 2008
Tuesday, January 29, 2008
Monday, January 28, 2008
Organization of Human Body Worksheet
1. Explain the difference between anatomy and physiology. Anatomy is the study of the structures of your brain, physiology is the study of the functions of the structures
2. Please organize the following structures in order from smallest too largest: system, tissue, organ, and cell. Cell, Tissue, Organ, and System.
3. In the term physiology the suffix -logy means what? study something.
4. What is the type of membrane that lines all of the passages leading the exterior? Cell membrane.
5. What do you call a mass of cells that all perform the same function? Tissue.
6. What type of tissue is specialized for the conduction of nerve impulses? Nerve Tissue.
7. The term epidermis contains a prefix and a root term. What is the root in this word and what does it mean? What is the prefix in this word and what does it mean? Derm - skin
8. The term cavity appears frequently in this lesson. What does it mean?
9. Name the four main types of tissue and describe their function. Epidermis-covers entire bodies; Connective tissue-supports and protects; Muscle-specialized for contraction; Nerve-specialized for the conduction of neural impulse.
10. A cell is made of cytoplasm except for the nucleus, which is made of _______
__________. Don't know this one.
11. What type of membrane lines joint cavities and outer surfaces of bones? Fibrous Membrane.
12. What is an organ system? When two or more tissues combine; A group of organs specialized to perform a major body program.
13. Name the five types of membranes and where each is located. Cutaneous membrane- all over; Mucous Membrane-Lines all passageways into the body; Fibrous Membrane-Lines all joints; Serous membrane-Lines closed cavities; Fascia Membrane-Covers muscles-blood vessels.
14. What is the function of the cell membrane? The nucleus? To protect the cell.
15. The Cutaneous membrane is made of two distinct layers. Name each of these layers and describe what they are made of. Epidermis-it’s harder skin n places where there’s more pressure. Dermis-lubricates hair and skin, regulates body temperature.
2. Please organize the following structures in order from smallest too largest: system, tissue, organ, and cell. Cell, Tissue, Organ, and System.
3. In the term physiology the suffix -logy means what? study something.
4. What is the type of membrane that lines all of the passages leading the exterior? Cell membrane.
5. What do you call a mass of cells that all perform the same function? Tissue.
6. What type of tissue is specialized for the conduction of nerve impulses? Nerve Tissue.
7. The term epidermis contains a prefix and a root term. What is the root in this word and what does it mean? What is the prefix in this word and what does it mean? Derm - skin
8. The term cavity appears frequently in this lesson. What does it mean?
9. Name the four main types of tissue and describe their function. Epidermis-covers entire bodies; Connective tissue-supports and protects; Muscle-specialized for contraction; Nerve-specialized for the conduction of neural impulse.
10. A cell is made of cytoplasm except for the nucleus, which is made of _______
__________. Don't know this one.
11. What type of membrane lines joint cavities and outer surfaces of bones? Fibrous Membrane.
12. What is an organ system? When two or more tissues combine; A group of organs specialized to perform a major body program.
13. Name the five types of membranes and where each is located. Cutaneous membrane- all over; Mucous Membrane-Lines all passageways into the body; Fibrous Membrane-Lines all joints; Serous membrane-Lines closed cavities; Fascia Membrane-Covers muscles-blood vessels.
14. What is the function of the cell membrane? The nucleus? To protect the cell.
15. The Cutaneous membrane is made of two distinct layers. Name each of these layers and describe what they are made of. Epidermis-it’s harder skin n places where there’s more pressure. Dermis-lubricates hair and skin, regulates body temperature.
Tuesday, January 15, 2008
1. Root: adip
Meaning: fat
Term: adipose
Definition: Relating to animal fat
Sentence:
2. Root: bio
Meaning: life
Term: biopsy
Definition: The removal and examination of tissue, cells, or fluids from the living body
Sentence:
3. Root: capit
Meaning: head
Term: decapitate
Definition: To cut off the head
Sentence:
4. Root: cephal
Meaning: head
Term: cephalad
Definition: Toward the head or anterior end of the body
Sentence:
5. Root: corp
Meaning: body
Term: corpus
Definition: the body of an animal or person, especially dead
Sentence:
6. Root: crani
Meaning: skull
Term: cranium
Definition: the part that encloses the brain
Sentence:
7. Root: dentMeaning: toothTerm: dentalDefinition: of or relating to the teeth or dentistrySentence:
8. Root: histMeaning: tissueTerm: histologyDefinition: deals w/ the minute structure of animal and plant tissuesSentence:
9. Root: later
Meaning: side
Term: lateral
Definition: of, or relating to the side
Sentence:
10. Root: ocul
Meaning: eye
Term: oculist
Definition: One skilled in treating diseases in the eye.
Sentence:
11. Root: oste
Meaning: bone
Term: osteoblast
Definition: A bone forming cell
Sentence:
12. Root: phag
Meaning: eat
Term: phagocyte
Definition: A cell that engulfs and consumes foreign material and debris
Sentence:
13. Root: pleur
Meaning: side
Term: pleura
Definition: The delicate serous membrane that lines each half of the thorax of mammals and is folded back over the surface of the lung of the same side
14. Root: quad
Meaning: four
Term: quadriceps
Definition: The greater extensor muscle of the front of the thigh that is divided into four parts
15. Root: stern
Meaning:
Term:
Definition:
Sentence:
16. Root: ab
Meaning: without
Term: abasia
Definition: Inability to walk due to muscle coordination.
17. Root: ad
Meaning: toward
Term: adrenal
Definition: Of relating to or derived from the adrenal glands or their secretions
18. Root: angi
Meaning: vessel
Term: angiography
Definition: the radiographic visualization of the blood vessels after injection of a radiopaque substance
19. Root: auto
Meaning: self
Term: autograft
Definition: A tissue or organ that is transplanted from one part to another of the same body
20. Root: centi
Meaning: hundred
Term: centimeter
Definition: one hundredth part of
21. Root: circum
Meaning: around
Term: circumflex
Definition: curving around
22. Root: dextro
Meaning: right
Term: dextrad
Definition: To or toward the right side
Sentence:
23. Root: epi
Meaning: upon
Term: epigastric
Definition: of, relating to, supplying, or draining the anterior walls of the abdomen
24. Root: ex
Meaning: out of
Term: excision
Definition: the act or procedure of removing by or as if by cutting out
25. Root: inter
Meaning: between
Term: interrenal
Definition: between the kidneys
26. Root: non
Meaning: not
Term: nonviable
Definition: not capable of living or developing
27. Root: ortho
Meaning: straight
Term: orthopedic
Definition: marked by or affected with a skeletal deformity, disorder, or injury
28. Root: path
Meaning: disease
Term: pathology
Definition: The study of the essential nature of diseases and especially of the structural and functional changes produced by them
29. Root: pseudo
Meaning: false
Term: pseudopod
Definition: the temporary projection of the cytoplasm of certain cells
30. Root: sinistro
Meaning: left
Term: sinistrad
Definition: toward the left side
31. Root: cide
Meaning: kill
Term: aborticide
Definition: a drug that causes abortion.
32. Root: itis
Meaning: inflame
Term: hepatitis
Definition: inflammation of the liver
33. Roots: logy
Meaning: study of
Term: histology
Definition: deals w/ the minute structure of animal and plant tissues
34. Root: meter
Meaning: measure
Term: pedometer
Definition: An instrument usually in watch form that records the distance a person covers on foot by responding to the body motion at each step
35. Root: plasty
Meaning: formed
Term: osteoplasty
Definition: plastic surgery on bone
36. Root: scope
Meaning: examine
Term: otoscope
Definition: an instrument w/ lighting and magnifying systems used for visual examination of the tympanic membrane and the canal connecting it to the exterior of the body
Meaning: fat
Term: adipose
Definition: Relating to animal fat
Sentence:
2. Root: bio
Meaning: life
Term: biopsy
Definition: The removal and examination of tissue, cells, or fluids from the living body
Sentence:
3. Root: capit
Meaning: head
Term: decapitate
Definition: To cut off the head
Sentence:
4. Root: cephal
Meaning: head
Term: cephalad
Definition: Toward the head or anterior end of the body
Sentence:
5. Root: corp
Meaning: body
Term: corpus
Definition: the body of an animal or person, especially dead
Sentence:
6. Root: crani
Meaning: skull
Term: cranium
Definition: the part that encloses the brain
Sentence:
7. Root: dentMeaning: toothTerm: dentalDefinition: of or relating to the teeth or dentistrySentence:
8. Root: histMeaning: tissueTerm: histologyDefinition: deals w/ the minute structure of animal and plant tissuesSentence:
9. Root: later
Meaning: side
Term: lateral
Definition: of, or relating to the side
Sentence:
10. Root: ocul
Meaning: eye
Term: oculist
Definition: One skilled in treating diseases in the eye.
Sentence:
11. Root: oste
Meaning: bone
Term: osteoblast
Definition: A bone forming cell
Sentence:
12. Root: phag
Meaning: eat
Term: phagocyte
Definition: A cell that engulfs and consumes foreign material and debris
Sentence:
13. Root: pleur
Meaning: side
Term: pleura
Definition: The delicate serous membrane that lines each half of the thorax of mammals and is folded back over the surface of the lung of the same side
14. Root: quad
Meaning: four
Term: quadriceps
Definition: The greater extensor muscle of the front of the thigh that is divided into four parts
15. Root: stern
Meaning:
Term:
Definition:
Sentence:
16. Root: ab
Meaning: without
Term: abasia
Definition: Inability to walk due to muscle coordination.
17. Root: ad
Meaning: toward
Term: adrenal
Definition: Of relating to or derived from the adrenal glands or their secretions
18. Root: angi
Meaning: vessel
Term: angiography
Definition: the radiographic visualization of the blood vessels after injection of a radiopaque substance
19. Root: auto
Meaning: self
Term: autograft
Definition: A tissue or organ that is transplanted from one part to another of the same body
20. Root: centi
Meaning: hundred
Term: centimeter
Definition: one hundredth part of
21. Root: circum
Meaning: around
Term: circumflex
Definition: curving around
22. Root: dextro
Meaning: right
Term: dextrad
Definition: To or toward the right side
Sentence:
23. Root: epi
Meaning: upon
Term: epigastric
Definition: of, relating to, supplying, or draining the anterior walls of the abdomen
24. Root: ex
Meaning: out of
Term: excision
Definition: the act or procedure of removing by or as if by cutting out
25. Root: inter
Meaning: between
Term: interrenal
Definition: between the kidneys
26. Root: non
Meaning: not
Term: nonviable
Definition: not capable of living or developing
27. Root: ortho
Meaning: straight
Term: orthopedic
Definition: marked by or affected with a skeletal deformity, disorder, or injury
28. Root: path
Meaning: disease
Term: pathology
Definition: The study of the essential nature of diseases and especially of the structural and functional changes produced by them
29. Root: pseudo
Meaning: false
Term: pseudopod
Definition: the temporary projection of the cytoplasm of certain cells
30. Root: sinistro
Meaning: left
Term: sinistrad
Definition: toward the left side
31. Root: cide
Meaning: kill
Term: aborticide
Definition: a drug that causes abortion.
32. Root: itis
Meaning: inflame
Term: hepatitis
Definition: inflammation of the liver
33. Roots: logy
Meaning: study of
Term: histology
Definition: deals w/ the minute structure of animal and plant tissues
34. Root: meter
Meaning: measure
Term: pedometer
Definition: An instrument usually in watch form that records the distance a person covers on foot by responding to the body motion at each step
35. Root: plasty
Meaning: formed
Term: osteoplasty
Definition: plastic surgery on bone
36. Root: scope
Meaning: examine
Term: otoscope
Definition: an instrument w/ lighting and magnifying systems used for visual examination of the tympanic membrane and the canal connecting it to the exterior of the body
Monday, January 14, 2008
Term
Terms:
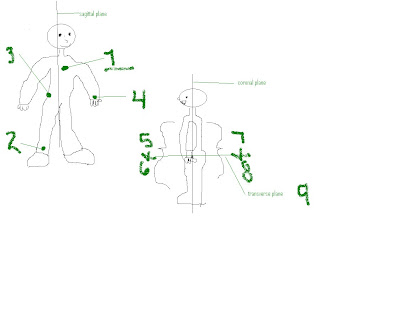
frontal plane - pertaining to the forehead.
sagittal plane - A plane or section that divides a structure into right and left portion.
transverse plane - At right angles to the long axis of a part; crosswise.
medial - Toward or near the midline.
superficial - near the surface.
superior - pertaining to a structure that is higher than another structure.
inferanterior - Pertaining to the front.
posterior - Toward the back; opposite of anterior.
distal - farther from the midline or orgin; opposite of proximal.
proximal - Closer to the midline or orgin; opposite of distal.
ior - Situated below something else; pertaining to the lower surface of a part.
flexion - Bending at a joint to decrease the angle between bones.
xtension - Movement increasing the angle between parts at a joint.
pronation - Movement of the palm downward or backward.
supine - lying on the back, face or front upward.
abduction - Movement of a body part away away from the midline.
adduction - Movement of a body part toward the midline
circumduction - Movement of a body part, such as a limb, so that the end follows a circular path. inversion - Movent in which the sole of the foot i sturned inward.
eversion - Outward turning movement of the sole of the foot.
elevation - Upward movement of a part of the body.
depression - Downward displacement.
anatomical position - A body postture with the body erect, the face forward, the arms at the sides with the palms facing forward, and the toes pointing straight ahead.
dorsal -pertaining to the back
ventral - Pertaining to the front and anterior
interior - further toward a center
exterior - being on the outer side
peripheral - pertaining to parts located near the surface or toward the outside.
lateral - pertaining to th eside.
frontal plane - pertaining to the forehead.
sagittal plane - A plane or section that divides a structure into right and left portion.
transverse plane - At right angles to the long axis of a part; crosswise.
medial - Toward or near the midline.
superficial - near the surface.
superior - pertaining to a structure that is higher than another structure.
inferanterior - Pertaining to the front.
posterior - Toward the back; opposite of anterior.
distal - farther from the midline or orgin; opposite of proximal.
proximal - Closer to the midline or orgin; opposite of distal.
ior - Situated below something else; pertaining to the lower surface of a part.
flexion - Bending at a joint to decrease the angle between bones.
xtension - Movement increasing the angle between parts at a joint.
pronation - Movement of the palm downward or backward.
supine - lying on the back, face or front upward.
abduction - Movement of a body part away away from the midline.
adduction - Movement of a body part toward the midline
circumduction - Movement of a body part, such as a limb, so that the end follows a circular path. inversion - Movent in which the sole of the foot i sturned inward.
eversion - Outward turning movement of the sole of the foot.
elevation - Upward movement of a part of the body.
depression - Downward displacement.
anatomical position - A body postture with the body erect, the face forward, the arms at the sides with the palms facing forward, and the toes pointing straight ahead.
dorsal -pertaining to the back
ventral - Pertaining to the front and anterior
interior - further toward a center
exterior - being on the outer side
peripheral - pertaining to parts located near the surface or toward the outside.
lateral - pertaining to th eside.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)